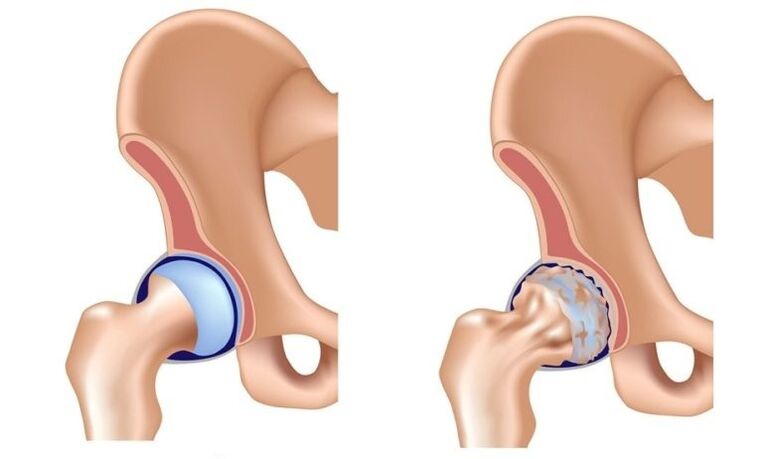
The joint nature of the hip joint (deformed joints, coronary heart disease, osteoarthritis) is a slow progressive degenerative disease that gradually eliminates the affected joints over time, with persistent pain and limiting mobility.
The disease affects people over the age of 40, and women get sick more than men.
In the overall structure of arthritis, the joint action of the hip joint is the main function.This is due to the widespread congenital pathology of the hip joints (dysplasia) and obvious physical fatigue, which are susceptible to impact.
Risk factors and causes of hip joints
In the pathological mechanism of joint development of hip joints, the main role is the change in the physicochemical characteristics of synovial (intra-articular) fluid, which results in it becoming denser and more viscous.This deteriorated the quality of her lubricating.As they move, the surfaces of the articular cartilage begin to rub against each other, becoming rough and covering the cracks.Small particles of clear cartilage are abandoned and fall into the joint cavity, resulting in the development of sterile (non-infectious) inflammation in it.As the disease enters the inflammatory process, bone tissue is attracted to the inflammation process, resulting in sterile necrosis of the cross sections of the femoral head and acetabular surface, forming bone plants (bone growth), enhancing inflammation and causing severe pain during exercise.
In the late stages of hip arthritis, inflammation is also thrown into the surrounding joints of the tissue (vascular, nerve, ligament, muscle), which can cause signs of arthritis in the surrounding people.As a result, the hip joint is completely destroyed, its function is lost, and its movement is stopped.This condition is called tonicity.
Causes of hip arthritis:
- Thighs congenital lips;
- hip dysplasia;
- Sterile necrosis of the femoral head;
- Peters' disease;
- Hip injury;
- infectious arthritis of the hip;
- adenotropic carcinoma (deformed osteoarthritis of the knee);
- Osteochondrosis;
- Too much weight;
- Professional sports;
- Flat feet
- curvature of the spine;
- A sedentary lifestyle.
Pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits features of the musculoskeletal system structure from his parents, which in this case may lead to hip arthritis.This explains the fact that families exist, with higher incidence rates than the general population.
The form of disease
According to the cause, the joint nature of the hip joint is divided into primary and secondary.Secondary arthritis develops in the context of the hip joint or other diseases in which it is injured.The main form is not related to previous pathology, and the reason for its development is usually impossible, in which case they talk about idiopathic arthritis.
Coksartrosis is one or both.
stage
Three stages (degrees) are distinguished during hip arthritis:
- Initial pathological changes are slightly expressed, as long as timely and appropriate treatment is reversible.
- Progressive patrol - characterized by gradual increase in symptoms (joint pain and impairment of mobility), changes in joint tissue are already irreversible, but treatment can slow down the degeneration process.
- The final movement in the joint is lost, forming ankylosing movement.Only surgical treatment (replace joints with artificial remedies).
In 95% of cases, the operation of the worm ensures complete recovery of limb mobility and restores the patient's performance.
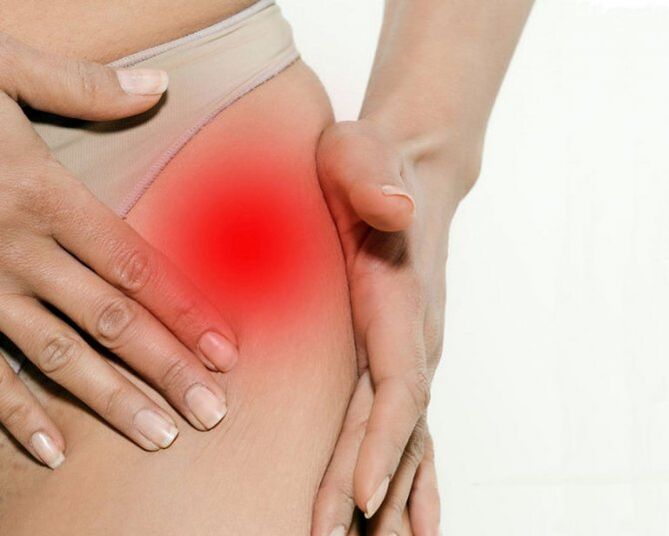
Symptoms of hip arthritis
Key signs of hip arthritis:
- Groin, hip and knee pain;
- The stiffness of the affected joint and the limitations of its mobility;
- la way;
- Kidnapping restrictions;
- Thigh muscle atrophy changes.
Some symptoms of hip joint articulation and their severity depend on the degree of the disease.
In the 1 degree joint of the hip joint, the patient complains about the pain in the affected joint under the influence of physical activity (long-term walking, running).In some cases, the pain is located in the knee or thigh area.After a short break, the pain disappeared on its own.The volume of limb movement is completely preserved and the gait will not be broken.The following changes are indicated on the X-ray:
- There is a slight reduction in imbalance in the cavity of the joint space;
- Bone plants are located on the inner edge of the rotation.
No changes in the neck and femoral head were detected.
With the second degree of hip joints, pain also occurs in a static state, including at night.After physical exercise, the patient began to move and formed a characteristic "duck" gait.Thus, painful pain occurs - after a long period of fixation, the first few steps cause pain and discomfort, then pass after a long load and then return.In the affected joints, the amount of movement (abduction, internal rotation) is limited.X-rays showed that the joint gap was uneven and its lumen was 50% standard.Bone plants are located in the inner and outer edges of the joint cavity, beyond the boundaries of the cartilage.Due to deformation, the profile of the femoral head becomes unbalanced.
With the degree of joint III of the painful hip joint, it is strong and constant, and does not stop at night.Walking is very difficult and the patient is forced to rely on crutches.The amount of movement in the affected joint was greatly limited and was later stopped completely.Due to the atrophy of the hip muscles, the pelvis deviates on the frontal plane and the limbs are shortened.In an attempt to make up for this shortening, patients on the walk were forced to refuse the body to the lesion, which further increased the load on the sore joints.On X-rays, multiple bone growth, significant stenosis of joint space, and significant increase in femoral head.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of hip joints is based on the results of clinical maps of the disease, medical examinations and instrumental studies, where the main value belongs to the visualization method - X-ray, computational or magnetic resonance imaging.They allow not only to determine the presence and assessment of the degree of the hip joint, but also to determine the possible causes of the disease (trauma, young osteolysis, Peters' disease).
The diagnosis of hip joint articulation with other diseases of the musculoskeletal system is quite complex.At the level II and III of the hip joint, muscle atrophy develops, which can lead to knee characteristics (knee disease) in knee drive or gonadal arthritis.To differentially diagnose these states, palpation of the knee and hip joints, the volume of movement was determined, and they were also examined by radiology.
In spinal diseases, in some cases, the spinal cord nerve roots that develop with pain syndrome are squeezed.The pain radiates to the area of the hip joint and mimics the clinical situation of its failure.However, the nature of pain in radicular syndrome is slightly different from that of hip joints:
- Pain is caused by weightlifting or rapid awkward exercise, not under the influence of physical fatigue.
- The pain is located in the gluteus muscles, not the groin area.
Using radiation syndrome, patients can calmly extend their legs to one side, while in the joints of the hip joint, kidnapping is limited.The characteristic signs of radiation syndrome are positive symptoms of tension – severe pain when trying to straighten the patient’s back.
Hip joints can affect people over 40 years old, and women get sick more frequently than men.
The joint nature of the hip joint should also be distinguished from the loyal capsule (tube flexor).Within a few weeks, tiger cystitis develops faster.Usually, he had significant physical fatigue or injury before.In this disease, the pain is more pronounced than hip arthritis.At the same time, shortening of the limb and limiting its mobility was not detected.
The clinical manifestations of atypical reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis may be similar to those of hip arthritis.However, when walking does not intensify, pain occurs mainly at night or at rest, but instead, the pain decreases.In the morning, the patient noticed stiffness in the joints and passed a few hours later.
Treat hip joints
Orthopedic treatment of hip joints.Conservative therapies are pointed out with the degree of I and II disease.With obvious pain syndrome, the patient prescribed non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs in a short period of time.They should not be accepted for a long time, because they can not only negatively affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but also inhibit the regeneration ability of hyaluron cartilage.
In treatment options for hip arthritis, they include cartilage protectors and vasodilators, which are the best chance to restore cartilage tissue damage.There are obvious muscle cramps and a central muscle relaxant may be required.
In those cases, when pain syndrome cannot be prevented with non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs, please resort to intra-articular injection of corticosteroids.
Local treatment of hip joints with warming ointment can reduce muscle cramps and reduce pain due to distraction.
In complex therapies of hip joint joints, physical therapy methods are also used:
- Magnetic therapy;
- attribution;
- uhf;
- laser therapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- massage;
- Medical gymnastics;
- Manual therapy.
Dietary nutrition for hip joint articular joints is designed to correct the normalization of weight and metabolic processes.Losing weight reduces the load on the hip, which slows down the disease progression.
To remove the affected joint, the doctor may advise the patient to take a cane or crutch.
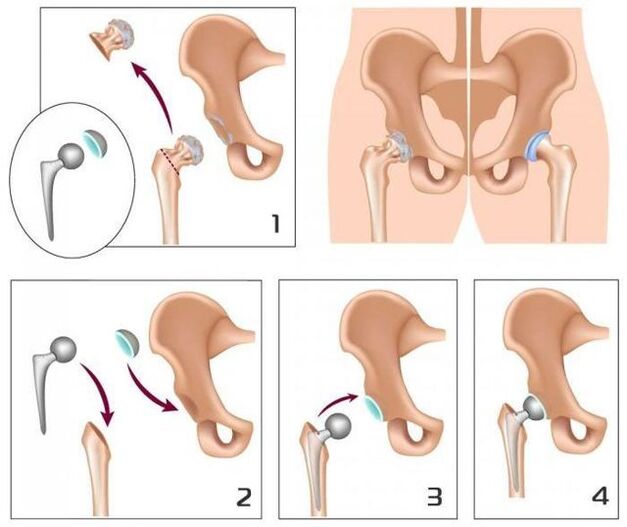
With the III level of hip joint nature, conservative treatment is inefficient.In this case, it is possible to improve the patient's condition and return to normal mobility through surgical intervention - replacing the damaged joint with artificial (the thoughts of the main mind in the joint).
Possible consequences and complications
The most serious complication of progressive joint arthropathy is disability due to loss of joint movement.With bilateral coksartrososis, patients lose the ability to move independently and require continuous care.Lying in a bed in one position for prolonged periods creates a premise for the occurrence of stagnant (muscular) pneumonia, which is difficult to succumb and can lead to death.
Pathology is not inherited, but children inherit features of the musculoskeletal system structure from their parents, which may lead to hip arthritis.
forecast
Hip arthritis is a progressive chronic disease that can only be completely cured when the cause of the disease is eliminated.In other cases, the therapy allows you to slow down your speed, but over time, it requires implantation of the hips.In 95% of cases, such procedures can completely restore limb mobility and restore patient performance.Modern prostheses have a service life of 15-20 years, after which they are replaced.
prevention
The purpose of preventing hip arthritis is to eliminate the causes that may cause the development of this disease, including:
- Timely detect and treat hip diseases and injuries;
- Reject a sedentary lifestyle, regularly, but not excessive physical exercise;
- Weight control;
- Rational nutrition;
- Reject bad habits.